
There are 16 districts where the share of the population with a low level of education exceeds that with an average level of education. At the national level, by specific weight, the population with an average level of education dominates, but the population with a low level is next to it – 43.5 and 40.5 percent.
On January 31, the National Institute of Statistics released the second and final series of preliminary census results for December 1, 2021. The data are published by county, which increases the geographic area and the ability to analyze changes that have occurred between two censuses. Three characteristics will be covered at the county level in three weekly articles: educational attainment, marital status, and ethnic composition. This first article is about the level of education.
- of the permanent population by the highest level of complete education
- permanent population by ethnicity and level of complete education
- the permanent population of 2 years and older by level of education is the following and
- This was followed by the permanent population older than 2 years who attended courses at the educational institution by ethnicity and level of education.
Unfortunately, in none of the tables, these characteristics of education are also given by five-year age groups, which significantly reduces the amount of knowledge and comparability in the territorial profile.
The classification uses three levels of education, which we also meet in international practice: high, medium and low. Higher education is the first level, the second level includes post-secondary education and master’s level, high school or vocational level of apprentice and Low secondary, elementary, preschool and non-degree levels are included. In districts with a larger share of the young population (0-19 years) and graduates of secondary schools or gymnasiums, there will be a larger share. The results published in the first series of preliminary results on December 31, 2022, were only for the entire population of the country without territorial coverage. We now have county-level data, and this helps us better understand the realities of the country in terms of national averages, but with the aforementioned caveat of the entire county population without age distribution.
The population with a higher degree dominates in terms of share at the national level environment education, but there is a low-level population nearby – 43.5 and 40.5 percent. Graduates of higher educational institutions make up 16 percent. The dominance of the middle level is observed in 25 districts and in the capital, and in some of them it is significant, in districts located mainly in the south of the country. However, there are 16 districts in which the share of the population with a low level of education exceeds the share of the population with an average level of education. And they are mainly located in the northeastern and southern regions of development. The connection between the level of economic, social and cultural development and the shares of the population with an average and low level of education is obvious. But there is also internal migration with a change of address and place of residence, which is more important for the educated population. Picked up and perhaps even the Middle, favorable migration to the more developed counties and to a large extent to the Capital. Above all, outward migration has also contributed to a large proportion of middle- and low-income populations in all counties due to the emigration of people with higher education, especially in the last 10 years, after the exhaustion of the huge waves of emigrants since the 1990s. and 2000-2010, Romania’s entry into the European Union in 2007 and subsequent years marking the peak of flows. Since these are the results of the census with a huge mass of data, no tables will be used that are inconvenient for the reader, but a graphical data formula will be used.
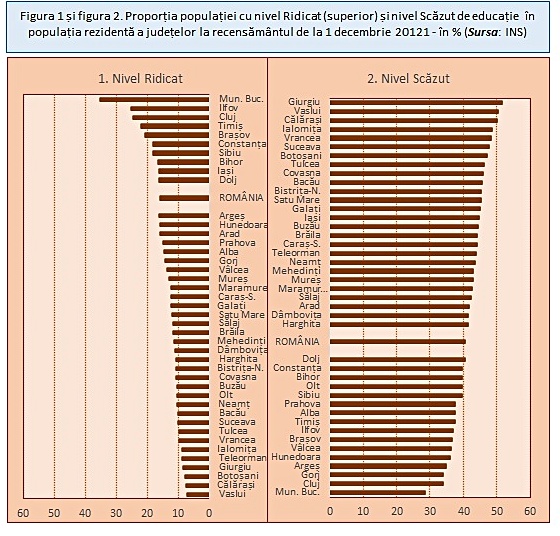
Figure 1 shows the share of the population with a high level of education (higher education) in the permanent population of the counties. The capital, especially the more developed counties, with prestigious university centers, networks of research and medical institutions, dominate the ranking, while counties in the northeastern region and three regions in the south of the country are in the most unfavorable positions. Looking at districts with proportions between 12 and 16 percent of the central third of the figure, observation can be helpful in understanding the positions. Among them are countries that, until 1990, for several decades had a high degree of industrialization (in huge combined and platforms of the steel, metallurgical, machine-building, petrochemical industries, in large shipyards, in the mining industry, etc.) and a significant workforce with higher education . For decades, they have left the economically active population due to retirement and are part of the permanent population with higher education. This applies to the districts of Braila, Karash-Severin, Galati, Hunedoara, Maramures, Prahova. The respective industries declined after 1989 for the most part, and the new industries are mainly located in the Bucharest-Ilfov economic region and in the three regions of Transylvania. The peculiarities of the level of education of men and women of the territorial profile are significant, we will not elaborate them in the article, but we will provide the reader with information about the share of the population with higher education in the figure in the appendix.
If we turn to the ranking according to the share of the population with low education in Figure 2, we find a parallel with the lower part of the ranking in Figure 1, with counties from the Nod-Est region and from the three regions in the south of the country. Transylvania includes only the districts of Covasna, Bistrica-Neseud and Satu Mare. At the bottom of the ranking, we find counties with higher shares at the high level as well as at the medium level (Gorge, Olt, Vilca, Hunedoara). It should not be forgotten that higher shares at the average level may come from differences in the age structure of the young population.
The placement of Covasna and Harghita counties at the bottom of the ranking for high levels of education, for both men and women, and at the top for low levels in the case of Covasna county, after important aid received from Hungary. government in the field of education is surprising. Perhaps some of the young people who studied and are studying in higher education institutions in Hungary to some extent prefer to settle in a neighboring country after graduation or in other countries. Read the whole article and comment on Contributors.ro
Source: Hot News
James Springer is a renowned author and opinion writer, known for his bold and thought-provoking articles on a wide range of topics. He currently works as a writer at 247 news reel, where he uses his unique voice and sharp wit to offer fresh perspectives on current events. His articles are widely read and shared and has earned him a reputation as a talented and insightful writer.