
10 years ago, about 100,000 babies were born in Romania in the first 6 months. Today, their number barely exceeds 70,000. Every year, 700 children (minors) and a very large number of children born abroad are born in our country.
Permanent departures from the country (last year was a record permanent emigration from Romania), especially in the case of women of childbearing age, massively affect the number of births. “Now they leave the country at an average age of 34,” said INS President Tudorel Andrej at the “Family Health and Birth” conference held at the Romanian Academy.
Watch the presentation by Professor Andrii Tudorel, President of INS, here

“It was said here that there are few births of young women in our country. Unfortunately, in the years 2002-2021, almost 700 children are born in our country every year. Which means a lot and shows the state of affairs that is happening both in the village and in the city, but especially in the countryside,” Andrii Tudorel also drew attention.
One in three underage mothers in Romania is also born to an underage mother, and 8 out of 10 mothers or pregnant women under the age of 18 no longer go to school, according to research by Save the Children. In addition, 45% of births registered among girls under the age of 15 in the European Union come from Romania, the country that ranks first in the EU for this indicator.
In addition, the average age at first birth for adolescent mothers from disadvantaged rural areas in Romania is 16 years for the first birth and 18 years for the second.
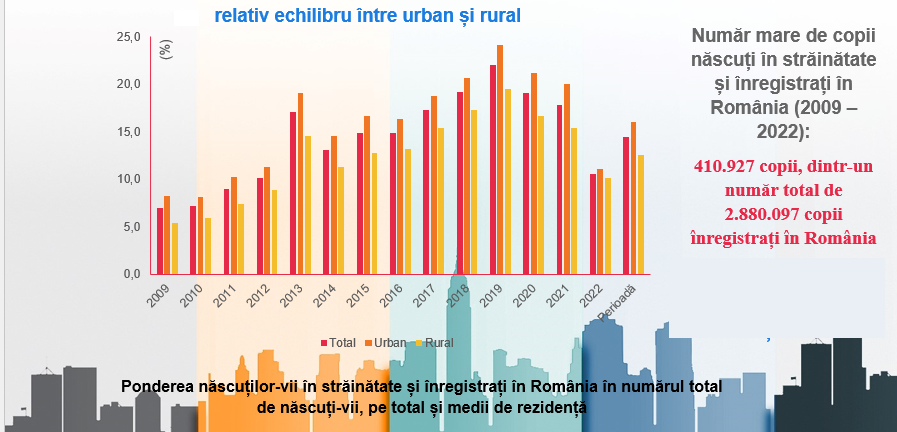
In the context of the low birth rate, the President of the INS also spoke about children born abroad and registered in Romania (between 2009 and 2022): their 410,927 children out of a total of 2,880,097 children registered in Romania.
Tudorel Andrii also presented a map with the distribution of children born abroad and registered in Romania by district, as well as the first 3 countries where they were born.

Below is the time share of children born outside the country in the total number of births
Some features of population reduction (RPL2021 vs. RPL2011)
- A decrease of 5.3% at the level of the entire population;
- Decrease by 8.4% of the population under 8 years;
- 5.7% decrease in the population under 10 years of age;
- The share of the adult population (15-64 years) decreases from 68.0% to 64.3%;
- The share of the adult population in the age group of 55-64 years decreases from 19.7% to 18.2%;
- The share of the population over 65 years old is growing from 16.1% to 19.6%.
Demographic aging index
121.2 elderly people (65 years and older) per 100 young people (up to 15 years old), more by approx. 20% in relation to the value of the indicator determined at RPL2011 (101.8).
Demographic dependence report
55.5 young and elderly per 100 adults compared to 47.0 in RPL 2011.
Migration
International migration significantly reduced the permanent population of Romania, especially in the first 20 years of the transition.
From 2031, those born after 1967 will become elderly.
The average age has increased
1990 – average age (34.5; 33.4 (M); 35.6 (W))
2020 – average age (42.2; 40.6(M); 43.9(M))
1990 – 2020: Romania’s permanent population aged by 7.7 years (22%)
The phenomenon of aging is more pronounced among the female population (8.3 years compared to 7.2 years for the male population)
At the beginning of this century, the female fertility rate was 5 children per woman
The first component of the natural movement is the birth rate, which is measured by the number of live births per 1,000 inhabitants, Academician Volodymyr Trebici, one of the greatest Romanian demographers, notes in his book “Demography”.
More precisely, the birth rate of the female population is measured by the number of live births among the female population of childbearing age, which is considered to be between 15 and 50 years of age. The measurement is carried out according to specific birth rates by age; a synthetic indicator – a cyclical fertility index or total fertility rate, which expresses the number of children born to a woman in the period of 15-50 years.
as part of the demographic transition, the birth rate of the female population systematically decreased: at the beginning of our century, it amounted to 5 children per woman; around 1930 it was reduced to 4 copies. After the Second World War, the total birth rate continuously decreased: from 2.7 children. in 1950 to 1.9 children in 1965-1966.
For simple generational replacement, a couple must produce 2.15 children for a daughter to survive to ensure reproduction.
After measures adopted at the end of 1966 aimed, in particular, at a sharp restriction of abortion, the birth rate recovered. The trend did not persist, which prompted the totalitarian communist state to adopt new restrictive measures regarding abortions, writes Volodymyr Trebichi
In 1989, the total fertility rate was 2.19 children, exceeding the reproduction rate of generations; since 1990, the indicator has been decreasing, being below the replacement threshold. Despite the established restrictions, abortion was widely practiced as the only method of family planning. The negative effect was a very high level of maternal and child mortality.
Source: Hot News
Ashley Bailey is a talented author and journalist known for her writing on trending topics. Currently working at 247 news reel, she brings readers fresh perspectives on current issues. With her well-researched and thought-provoking articles, she captures the zeitgeist and stays ahead of the latest trends. Ashley’s writing is a must-read for anyone interested in staying up-to-date with the latest developments.